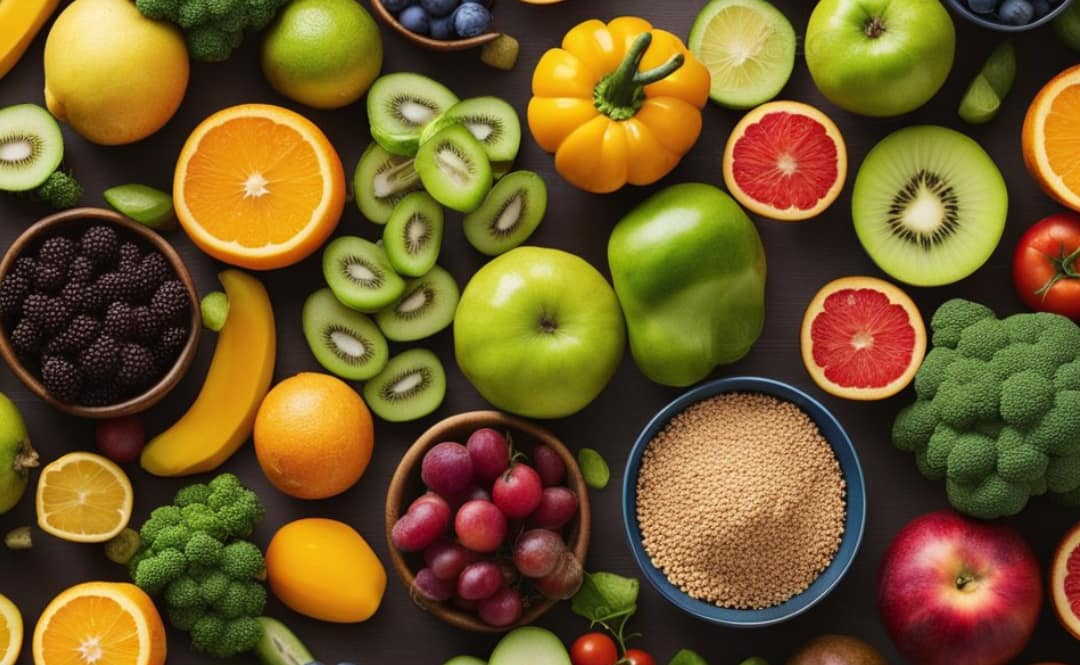
Building a gut-friendly diet is more than a fleeting trend; it’s a transformative journey toward digestive wellness and balanced nutrition that beckons you with the promise of improved health and vitality. The intricate dance of nutrients, fibers, and probiotics plays out in the vast theater of our gastrointestinal tract, where every meal contributes to the complex narrative of our well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we will unveil the secrets to nurturing your digestive system with the right foods, harmonizing your body’s needs with the rhythms of a diet designed for gut health.
As we delve into the art of crafting a gut-friendly diet, we embrace the diversity of wholesome ingredients that not only satiate our taste buds but also fortify our body’s inner workings. The symphony of prebiotic-rich foods, hearty grains, and fermented delights creates a melody that resonates with our microbiome, the community of microorganisms that play a pivotal role in our digestive health. By understanding the interplay between these components, we set the stage for a flourishing gut that supports our overall wellness.
Navigating the world of digestive health can seem daunting, yet it is a path paved with delicious possibilities and insightful discoveries. Whether you’re battling with sensitivities, looking to boost your immune system, or simply aiming to maintain a healthy lifestyle, the principles of building a gut-friendly diet offer a beacon of hope and a blueprint for success. Join us as we explore the essential elements of a diet that respects and enhances your digestive health, ensuring that every forkful is a step toward a happier, healthier you.
Overview
When it comes to our overall health and well-being, our gut plays a crucial role. Our gut health is directly linked to our immune system, mental health, and even our skin health. Therefore, it is important that we pay attention to what we eat and build a gut-friendly diet. In this article, we will discuss the importance of gut health and provide some tips on how to build a gut-friendly diet.

The first step in building a gut-friendly diet is understanding what gut health is and why it is important. Our gut is home to trillions of bacteria, both good and bad. When the balance between these bacteria is disrupted, it can lead to a range of health issues such as digestive problems, inflammation, and even autoimmune diseases. Therefore, maintaining a healthy balance of gut bacteria is crucial for our overall health and well-being.
One of the key factors in maintaining a healthy gut is our diet. The food we eat has a direct impact on the balance of bacteria in our gut. In the next section, we will discuss some of the foods that are beneficial for gut health and how to incorporate them into our diet.
Understanding Gut Health for Building a Gut-Friendly Diet
When it comes to building a gut-friendly diet, it is important to understand the role of our gut health. Our gut is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiome. This microbiome plays a crucial role in our overall health, including our immune system, digestion, and even mental health.
The Microbiome and Its Role
The gut microbiome is made up of a variety of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and more. These microorganisms play a crucial role in our gut health by helping to break down food, produce vitamins and other essential nutrients, and even protect against harmful pathogens.
One of the most important components of the gut microbiome is the good bacteria, also known as probiotics. These bacteria help to maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms in the gut, which is essential for optimal gut health.
Factors Affecting Gut Health
There are a variety of factors that can affect the health of our gut microbiome. These include:
-
Diet: A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can negatively impact the gut microbiome, while a diet rich in whole foods, fiber, and fermented foods can promote a healthy gut microbiome.
-
Antibiotics: While antibiotics can be life-saving in certain situations, they can also kill off both good and bad bacteria in the gut, which can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome.
-
Stress: Chronic stress can have a negative impact on the gut microbiome, leading to inflammation and other health issues.
-
Lack of sleep: Poor sleep habits can also negatively impact the gut microbiome, as sleep plays a crucial role in regulating the immune system and other bodily functions.
By understanding the role of the gut microbiome and the factors that can affect its health, we can make informed choices when it comes to building a gut-friendly diet. Incorporating a variety of whole foods, fiber, and fermented foods, while also managing stress and getting adequate sleep, can all contribute to a healthy gut microbiome and overall gut health.
Key Dietary Components for a Healthy Gut

Maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall health and well-being. A gut-friendly diet is a diet that promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and reduces inflammation. In this section, we will discuss the key dietary components for a healthy gut.
Importance of Fiber
Fiber is an essential component of a gut-friendly diet. It is a type of carbohydrate that our body cannot digest, but it plays a crucial role in our digestive system. Fiber helps to regulate bowel movements, maintain healthy gut bacteria, and reduce inflammation. It also helps to lower cholesterol levels and control blood sugar levels.
Fiber can be found in a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds. It is recommended that adults consume at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day.
Role of Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics are live bacteria that are beneficial for our gut health. They can be found in fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi. Probiotics help to maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which can improve digestion and reduce inflammation.
Prebiotics, on the other hand, are a type of fiber that feeds the beneficial gut bacteria. They can be found in foods such as onions, garlic, bananas, and asparagus. Consuming prebiotics can help to promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and improve gut health.
Identifying Nutrient-Dense Foods
In addition to fiber, probiotics, and prebiotics, it is important to consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods to maintain a healthy gut. Nutrient-dense foods are foods that are high in nutrients but relatively low in calories.
Some examples of nutrient-dense foods include:
- Dark leafy greens such as spinach and kale
- Berries such as blueberries and raspberries
- Whole grains such as quinoa and brown rice
- Lean protein sources such as chicken, fish, and tofu
- Healthy fats such as avocado and nuts
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help to support a healthy gut and overall health.
In conclusion, a gut-friendly diet includes a variety of foods that promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and reduce inflammation. Incorporating fiber, probiotics, prebiotics, and nutrient-dense foods into your diet can help to support a healthy gut and improve overall health.
Foods to Include and Avoid

When it comes to building a gut-friendly diet, the foods we choose to include and avoid can have a significant impact on our gut health. Here are some of the foods we recommend including and avoiding in your diet:
Probiotic-Rich Foods
Probiotic-rich foods contain live bacteria that can help promote a healthy gut microbiome. Some examples of probiotic-rich foods include:
- Kefir: a fermented milk drink that contains a variety of live bacteria and yeasts.
- Kombucha: a fermented tea that contains live bacteria and yeasts.
- Sauerkraut: fermented cabbage that contains live bacteria.
- Kimchi: a Korean dish made from fermented vegetables that contains live bacteria.
- Yogurt: a dairy product that contains live bacteria.
Including these foods in your diet can help promote a healthy gut microbiome and improve digestive health.
Prebiotic Foods That Nourish Gut Bacteria
Prebiotic foods are high in fiber and other nutrients that nourish the gut bacteria. Some examples of prebiotic foods include:
- Garlic: a vegetable that contains prebiotic fibers and other nutrients.
- Onions: a vegetable that contains prebiotic fibers and other nutrients.
- Bananas: a fruit that contains prebiotic fibers and other nutrients.
- Asparagus: a vegetable that contains prebiotic fibers and other nutrients.
- Jerusalem artichokes: a root vegetable that contains prebiotic fibers and other nutrients.
Including these foods in your diet can help promote a healthy gut microbiome by nourishing the beneficial bacteria in your gut.
Foods Linked to Poor Gut Health
Some foods can have a negative impact on our gut health. These include:
- Processed foods: foods that are heavily processed and contain additives and preservatives.
- Sugar: foods and drinks that contain added sugars.
- Artificial sweeteners: sugar substitutes that can disrupt the gut microbiome.
Avoiding these foods can help promote a healthy gut microbiome and improve digestive health.
By including probiotic-rich foods, prebiotic foods, and avoiding foods linked to poor gut health, we can promote a healthy gut microbiome and improve our overall health.
Impact of Diet on Digestive Health

As we all know, our diet plays a significant role in our digestive health. What we eat affects the way our bodies digest food, and can either promote or hinder our digestive system’s overall health. In this section, we will explore how our diet impacts our digestive health and how we can build a gut-friendly diet.
Managing Common Digestive Issues
Many people experience digestive issues such as bloating, gas, constipation, and diarrhea. These symptoms can be uncomfortable and even painful, but they can often be managed through dietary changes. For example, increasing fiber intake can help alleviate constipation, while reducing high-fat and high-sugar foods can help reduce bloating and gas. It’s essential to pay attention to our bodies and make adjustments to our diet accordingly.
Long-Term Benefits of a Gut-Friendly Diet
Maintaining a gut-friendly diet can have long-term benefits beyond just managing common digestive issues. Studies have shown that a healthy gut can reduce the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help improve our gut health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Building a gut-friendly diet takes time and effort, but it’s worth it for the long-term benefits. By making small changes to our diet, such as increasing fiber intake and reducing processed foods, we can improve our digestive health and overall well-being.
Creating a Gut-Friendly Meal Plan

When it comes to building a gut-friendly diet, meal planning is essential. Here are some tips to help you create a meal plan that supports a healthy gut.
Sample Meal Ideas
Including a variety of plant-based foods and whole grains in your meals can help promote healthy gut bacteria. Here are some meal ideas to get you started:
- Breakfast: Overnight oats with fruit and nuts, a smoothie bowl with spinach and berries, or avocado toast on whole grain bread.
- Lunch: A big salad with mixed greens, roasted vegetables, and a source of protein like tofu or chickpeas, a quinoa bowl with roasted vegetables and a tahini dressing, or a vegetable stir-fry with brown rice.
- Dinner: Grilled salmon with roasted vegetables, a lentil soup with whole grain bread, or a vegetable curry with brown rice.
Tips for Sustainable Eating Habits
Building a gut-friendly diet is not just about what you eat, but also how you eat. Here are some tips for creating sustainable eating habits:
- Eat mindfully: Pay attention to your hunger and fullness cues, and take time to enjoy your meals without distractions.
- Cook at home: Preparing meals at home allows you to control the ingredients and quality of your food.
- Plan ahead: Take some time each week to plan your meals and snacks, and prepare some healthy options ahead of time.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help support a healthy gut.
- Don’t forget about variety: Eating a variety of foods can help ensure you’re getting all the nutrients your body needs.
By incorporating these tips into your meal planning, you can create a balanced diet that supports healthy gut bacteria and overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions

What are the top foods recommended for maintaining a healthy gut?
We recommend incorporating a variety of plant-based foods into your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These foods are rich in fiber, which helps promote healthy digestion and can improve the balance of gut bacteria. Fermented foods such as kimchi, sauerkraut, kefir, and yogurt are also great sources of beneficial bacteria.
Which foods should be avoided to promote gut health?
It’s best to limit or avoid highly processed foods, added sugars, artificial sweeteners, and saturated and trans fats. These foods can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and contribute to inflammation in the gut. It’s also important to be mindful of any food intolerances or sensitivities that may be causing digestive issues.
How can one naturally increase beneficial gut bacteria?
In addition to incorporating fermented foods into your diet, you can also increase beneficial gut bacteria by consuming prebiotic-rich foods such as garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, bananas, and oats. Probiotic supplements can also be helpful, but it’s important to choose a high-quality product with strains that have been proven to be effective.
What are effective dietary strategies for healing gut inflammation?
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as leafy greens, berries, fatty fish, and turmeric can help reduce inflammation in the gut. It’s also important to avoid trigger foods that may be contributing to inflammation, and to consider working with a healthcare provider to identify any underlying conditions that may be causing inflammation. Adequate hydration and stress management can also play a role in reducing inflammation in the gut.
Final Thoughts
In the tapestry of nutritional wisdom, the threads of a gut-friendly diet weave a pattern of health that extends far beyond the confines of our digestive system. We’ve journeyed through the landscape of fibers, probiotics, and nutrient-dense foods, uncovering the profound impact that a balanced diet can have on our digestive wellness. As we draw this exploration to a close, it’s clear that the choices we make at the dining table can echo through the vast corridors of our health, resonating with the very essence of vitality.
Embracing the principles of a gut-friendly diet is not merely a fleeting engagement with healthy eating, but a lifelong commitment to nurturing the delicate balance within. It is a commitment that demands mindfulness and a willingness to listen to the subtle cues of our bodies. As you step forward from this point, armed with knowledge and inspired by the potential for transformation, remember that the journey to digestive wellness is a personal one, a mosaic of unique needs and preferences.
We invite you to continue experimenting with the ingredients and recipes that resonate with your body’s unique symphony, and to remain vigilant in your quest for a harmonious digestive environment. May the insights gleaned here serve as your compass, guiding you to a state of health where tranquility reigns supreme within your gut, and by extension, throughout your entire being. Here’s to the vibrant future that awaits on the other side of every mindful bite. Bon appétit and be well.